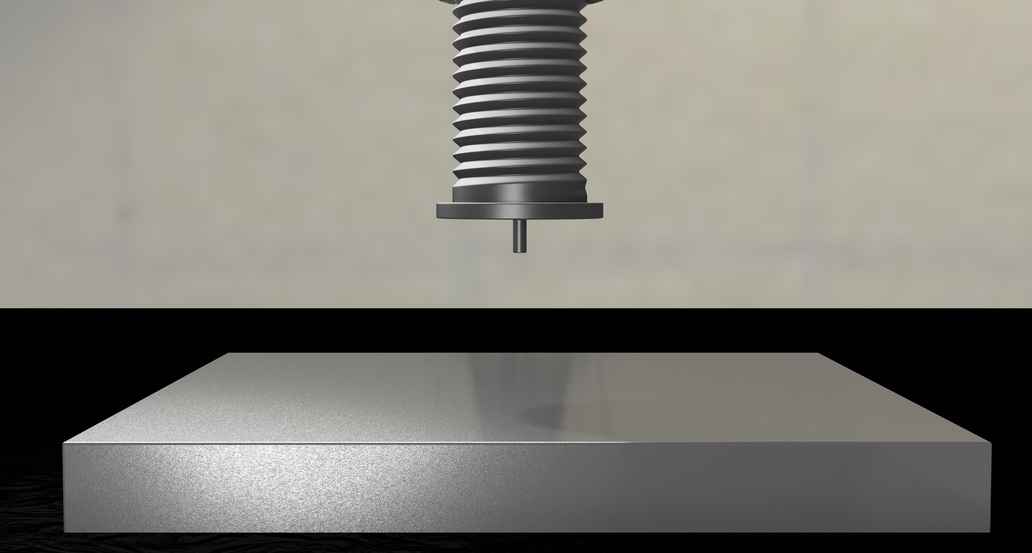
Stud Welding
Stud welding is a special form of arc welding and is used to create permanent connections between large workpieces and studs.
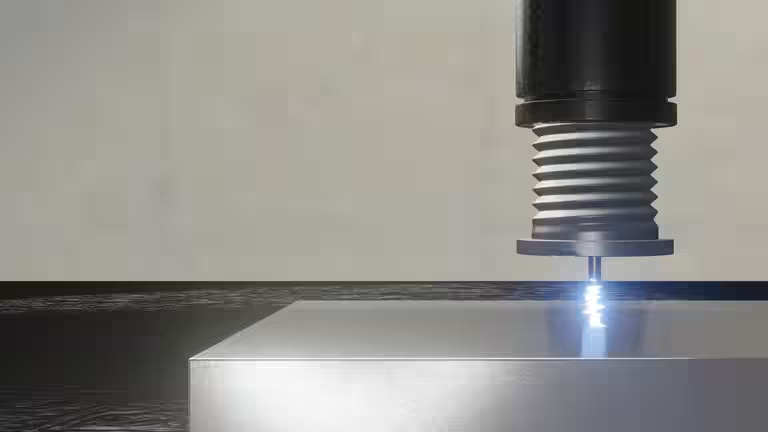
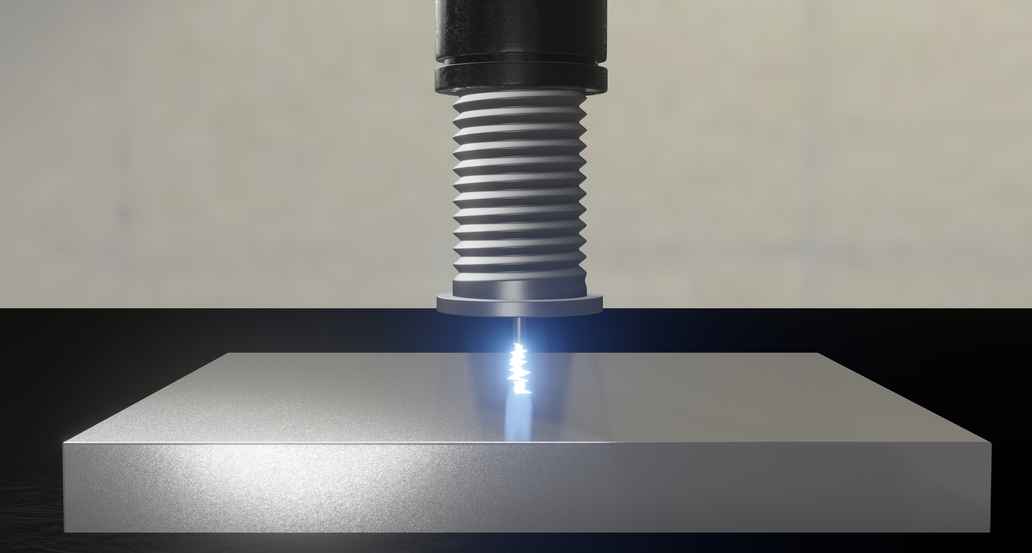
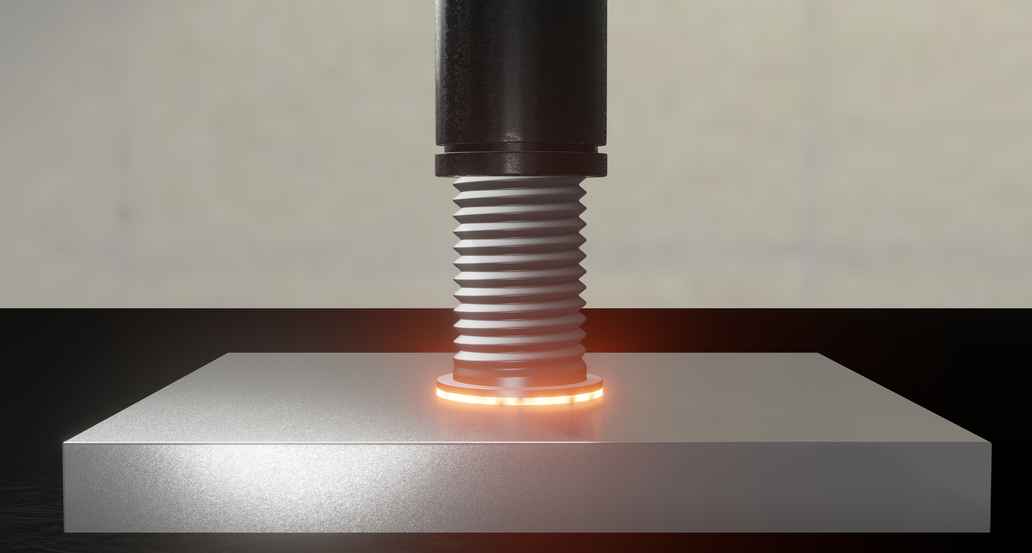
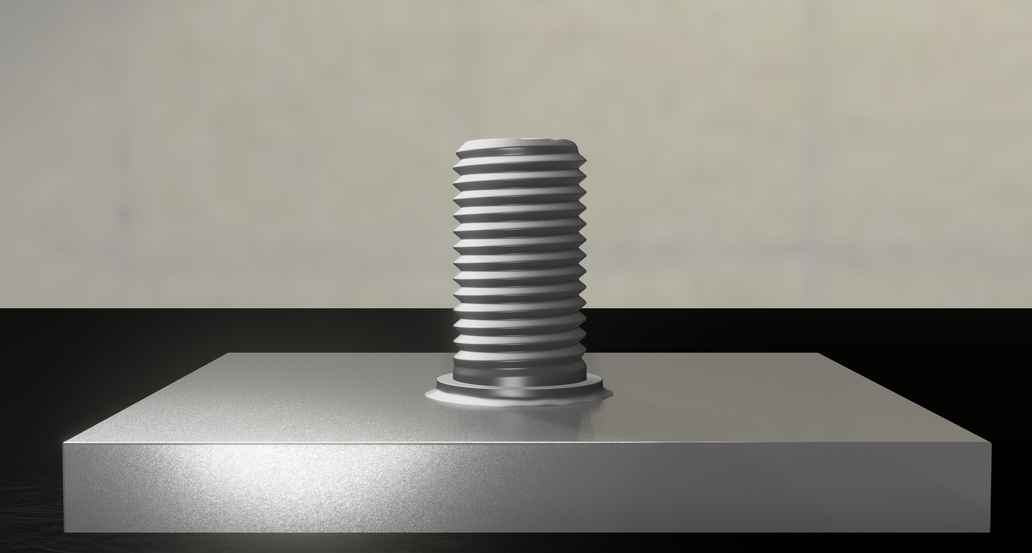
This process is very time-saving, because the arc is ignited directly between the workpiece and the stud or pin, with the arc inlet and outlet surfaces being melted. In the molten state, the two metal parts are joined together with slight pressure and in this way permanently bonded together.
To use stud welding, the surface must be electrically conductive. It is absolutely necessary, to remove paint, rust or scale, before welding. If the plate metals are galvanised, they must be checked in advance to ensure that they can be welded.
Stud arc welding is generally divided into tip ignition and drawn arc stud welding. Basically, both methods are identical, and only differ in the way in which the arc is ignited.
The advantages of stud welding
- Very short welding time
- Minor distortion
- Very solid connection
- No post-processing
- Economical welding process
- No additional filler material required
Tip ignition stud welding
In this procedure there must be a small tip on the underside of the stud. The arc ignites at this tip and melts it as well as the whole underside of the stud. The weld pool produced is adequate for joining the stud. The tip ignition procedure is a very quick welding method and is particularly suitable for thinner sheet thicknesses from 0.6 mm. Welding studs size M3 to M8 with a diameter between 2 and 10 mm are used.
This type of stud welding can be used in many and diverse ways. For example, it is used in the electrical industry, for building housings and enclosures, in facade construction and in apparatus construction.
Drawn arc stud welding
In the drawn arc procedure the stud is in direct contact with the workpiece. In this position, the stud is energised and therefore forms a closed electrical circuit with the workpiece. The arc required for the melting is produced by lifting the stud. The stud and workpiece are then joined in exactly the same way as with the tip ignition stud welding procedure.
This procedure is used for greater sheet thicknesses from 2mm. Studs with diameters from 2 to 22 mm (M24) are used. This type of drawn arc stud welding can also be used on many and diverse ways. For example, it is used in structural steelwork, in mechanical engineering, in boiler construction as well as in shipbuilding.



